Giardia intestinalis str. GS (GCA_000498735.1) Assembly and Gene Annotation
About Giardia intestinalis str. GS
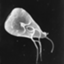
Giardia lamblia, also known as Giardia intestinalis, is a
flagellated parasitic microorganism, that colonizes and reproduces in
the small intestine, causing giardiasis. The parasite attaches to the
epithelium by a ventral adhesive disc or sucker, and reproduces via
binary fission. Giardiasis does not spread via the bloodstream, nor does
it spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but remains
confined to the lumen of the small intestine. Giardia trophozoites
absorb their nutrients from the lumen of the small intestine, and are
anaerobes. If the organism is split and stained, its characteristic
pattern resembles the familiar
"smiley face
" symbol. Chief pathways of
human infection include ingestion of untreated sewage, a phenomenon
particularly common in many developing countries; contamination of
natural waters also occurs in watersheds where intensive grazing occurs.
Giardia infections occur worldwide, however Giardia lamblia is the
most commonly identified intestinal parasite in the United States and
Canada among children in day care centers, hikers, family members and
immunocompromised adults. Approximately 20,000 cases per year in the
United States are reported.
(Text from Wikipedia, the free encyclopaedia.)
More information
General information about this species can be found in Wikipedia.
Statistics
Summary
| Assembly | ASM49873v1, INSDC Assembly GCA_000498735.1, |
| Database version | 114.1 |
| Golden Path Length | 12,009,633 |
| Genebuild by | |
| Genebuild method | Import |
| Data source | Integrated Genomics |
Gene counts
| Coding genes | 6,098 |
| Non coding genes | 166 |
| Small non coding genes | 164 |
| Long non coding genes | 2 |
| Gene transcripts | 6,264 |



![Follow us on Twitter! [twitter logo]](/i/twitter.png)
